You are here
Thu, 2015-01-08 20:48 — mdmcdonald
Information on vaccines to counter Ebola and other diseases
The Mission of this group is to follow the development of vaccines and other medications to counter Ebola and other diseases.
Add Content to this group
Members
| Kathy Gilbeaux | mdmcdonald | MDMcDonald_me_com | mike kraft |
Email address for group
vaccines_global@m.resiliencesystem.org



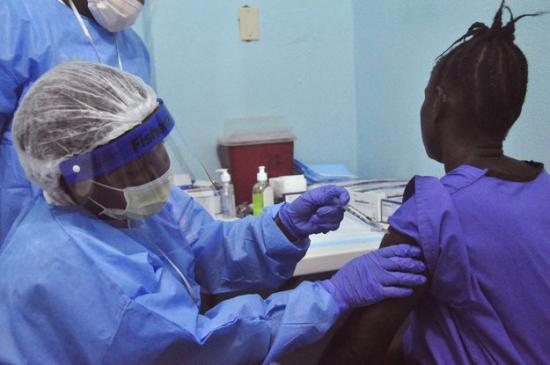
 Novavax's product is a glycoprotein recombinant nanoparticle vaccine adjuvanted with Matrix M (Ebola GP) to boost immune response. Conducted in Australia, the study will test the safety and immunogenicity of the vaccine, with and without the adjuvant, in 230 healthy adults ages 18 to 50. Subjects will be given two intramuscular injections 3 weeks apart....
Novavax's product is a glycoprotein recombinant nanoparticle vaccine adjuvanted with Matrix M (Ebola GP) to boost immune response. Conducted in Australia, the study will test the safety and immunogenicity of the vaccine, with and without the adjuvant, in 230 healthy adults ages 18 to 50. Subjects will be given two intramuscular injections 3 weeks apart....

Recent Comments